Publications
Here is a selected list of my publications. You can see all my publications on my Google scholar page.
2026
- RA-L
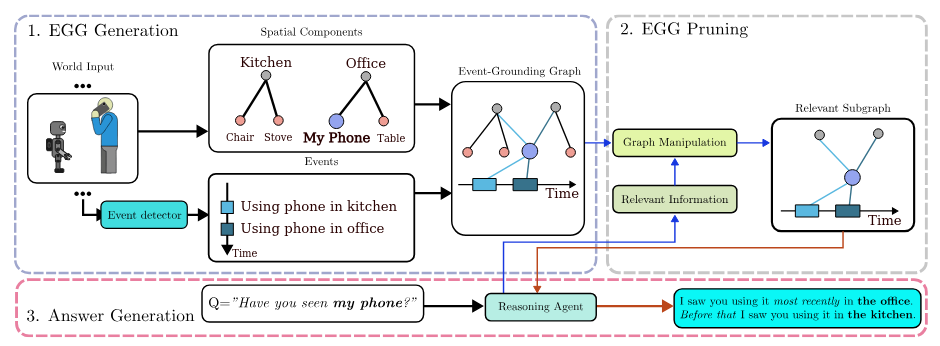 Event-Grounding Graph: Unified Spatio-Temporal Scene Graph from Robotic ObservationsPhuoc Nguyen, Francesco Verdoja, and Ville Kyrki2026
Event-Grounding Graph: Unified Spatio-Temporal Scene Graph from Robotic ObservationsPhuoc Nguyen, Francesco Verdoja, and Ville Kyrki2026A fundamental aspect for building intelligent autonomous robots that can assist humans in their daily lives is the construction of rich environmental representations. While advances in semantic scene representations have en- riched robotic scene understanding, current approaches lack a connection between spatial features and dynamic events; e.g., connecting the blue mug to the event washing a mug. In this work, we introduce the event-grounding graph (EGG), a framework grounding event interactions to spatial features of a scene. This representation allows robots to perceive, reason, and respond to complex spatio-temporal queries. Exper- iments using real robotic data demonstrate EGG’s capability to retrieve relevant information and respond accurately to human inquiries concerning the environment and events within. Furthermore, the EGG framework’s source code and evaluation dataset are released as open-source at: https://github.com/aalto-intelligent-robotics/EGG.
@misc{nguyen2026eventgroundinggraphunifiedspatiotemporal, bibtex_show = true, title = {Event-Grounding Graph: Unified Spatio-Temporal Scene Graph from Robotic Observations}, author = {Nguyen, Phuoc and Verdoja, Francesco and Kyrki, Ville}, year = {2026}, archiveprefix = {arXiv}, primaryclass = {cs.RO}, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.18697} }
2025
- IROS
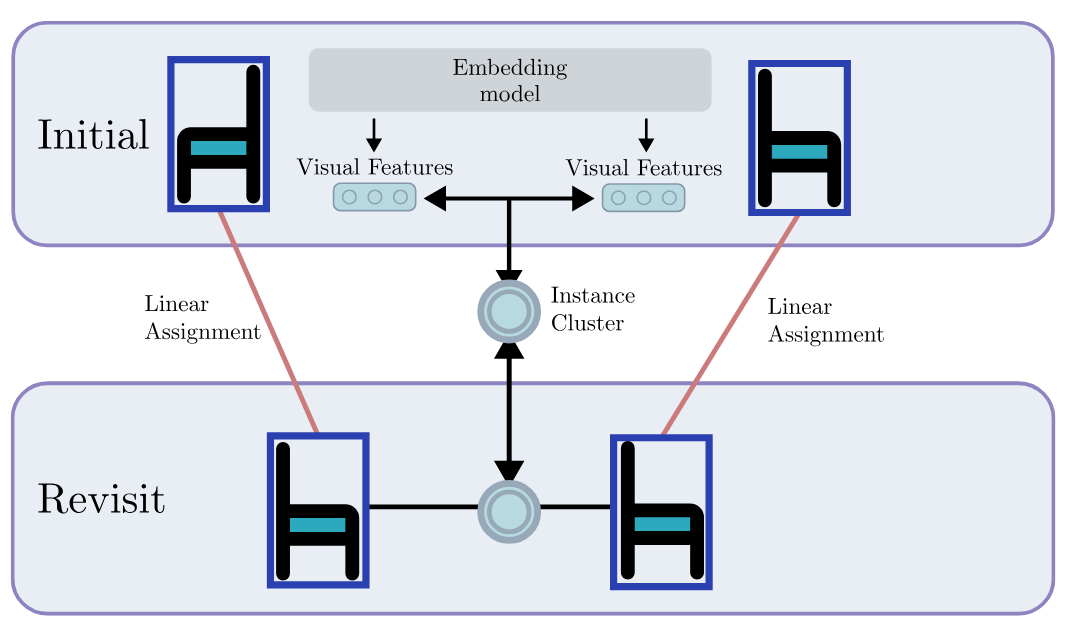 REACT: Real-time Efficient Attribute Clustering and Transfer for Updatable 3D Scene GraphPhuoc Nguyen, Francesco Verdoja, and Ville KyrkiIn 2025 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2025
REACT: Real-time Efficient Attribute Clustering and Transfer for Updatable 3D Scene GraphPhuoc Nguyen, Francesco Verdoja, and Ville KyrkiIn 2025 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2025Modern-day autonomous robots need high-level map representations to perform sophisticated tasks. Recently, 3D scene graphs (3DSGs) have emerged as a promising al- ternative to traditional grid maps, blending efficient memory use and rich feature representation. However, most efforts to apply them have been limited to static worlds. This work introduces REACT, a framework that efficiently performs real- time attribute clustering and transfer to relocalize object nodes in a 3DSG. REACT employs a novel method for comparing object instances using an embedding model trained on triplet loss, facilitating instance clustering and matching. Experimental results demonstrate that REACT is able to relocalize ob- jects while maintaining computational efficiency. The REACT framework’s source code will be available as an open-source project, promoting further advancements in reusable and up- datable 3DSGs
@inproceedings{nguyen2025react, selected = true, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2pHQ1tQE7C4&feature=youtu.be }, author = {Nguyen, Phuoc and Verdoja, Francesco and Kyrki, Ville}, booktitle = {2025 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS)}, title = {REACT: Real-time Efficient Attribute Clustering and Transfer for Updatable 3D Scene Graph}, year = {2025}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {2209-2216}, keywords = {Visualization;Three-dimensional displays;Source coding;Computational modeling;Memory management;Real-time systems;Computational efficiency;Intelligent robots;Autonomous robots}, doi = {10.1109/IROS60139.2025.11247273} }
2023
- Frontiers
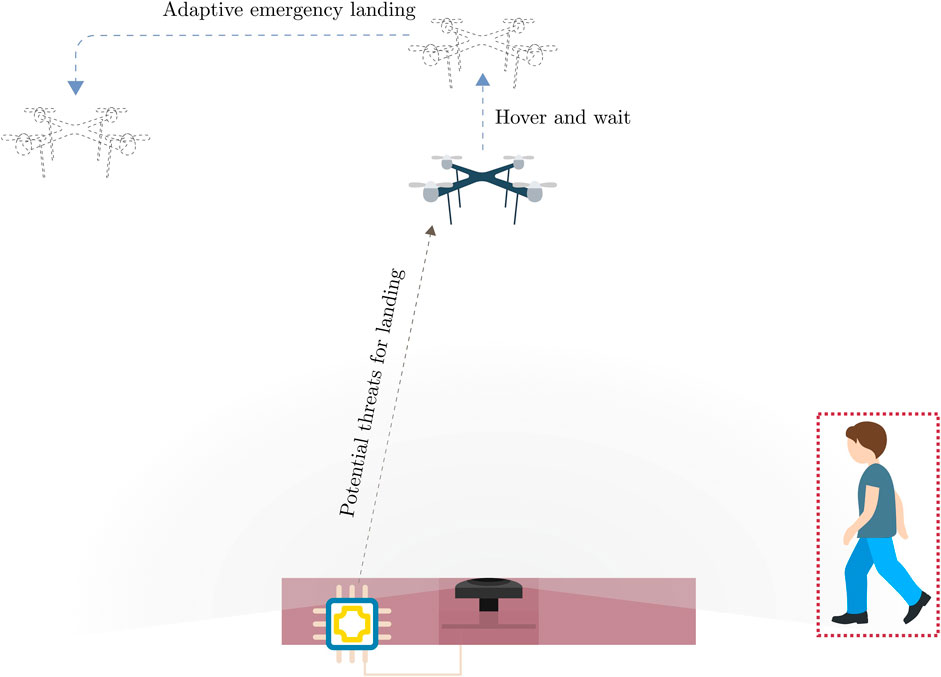 Vision-based safe autonomous UAV docking with panoramic sensorsPhuoc Thuan Nguyen, Tomi Westerlund, and Jorge Peña QueraltaFrontiers in Robotics and AI, 2023
Vision-based safe autonomous UAV docking with panoramic sensorsPhuoc Thuan Nguyen, Tomi Westerlund, and Jorge Peña QueraltaFrontiers in Robotics and AI, 2023The remarkable growth of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) has also sparked concerns about safety measures during their missions. To advance towards safer autonomous aerial robots, this work presents a vision-based solution to ensuring safe autonomous UAV landings with minimal infrastructure. During docking maneuvers, UAVs pose a hazard to people in the vicinity. In this paper, we propose the use of a single omnidirectional panoramic camera pointing upwards from a landing pad to detect and estimate the position of people around the landing area. The images are processed in real-time in an embedded computer, which communicates with the onboard computer of approaching UAVs to transition between landing, hovering or emergency landing states. While landing, the ground camera also aids in finding an optimal position, which can be required in case of low-battery or when hovering is no longer possible. We use a YOLOv7-based object detection model and a XGBooxt model for localizing nearby people, and the open-source ROS and PX4 frameworks for communication, interfacing, and control of the UAV. We present both simulation and real-world indoor experimental results to show the efficiency of our methods.
@article{nguyen2023visionsafeautonomousuav, selected = true, author = {Nguyen, Phuoc Thuan and Westerlund, Tomi and Peña Queralta, Jorge}, title = {Vision-based safe autonomous UAV docking with panoramic sensors}, journal = {Frontiers in Robotics and AI}, volume = {Volume 10 - 2023}, year = {2023}, url = { Https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/robotics-and-ai/articles/10.3389/frobt.2023.1223157 }, doi = {10.3389/frobt.2023.1223157}, issn = {2296-9144} }
- FinDrones
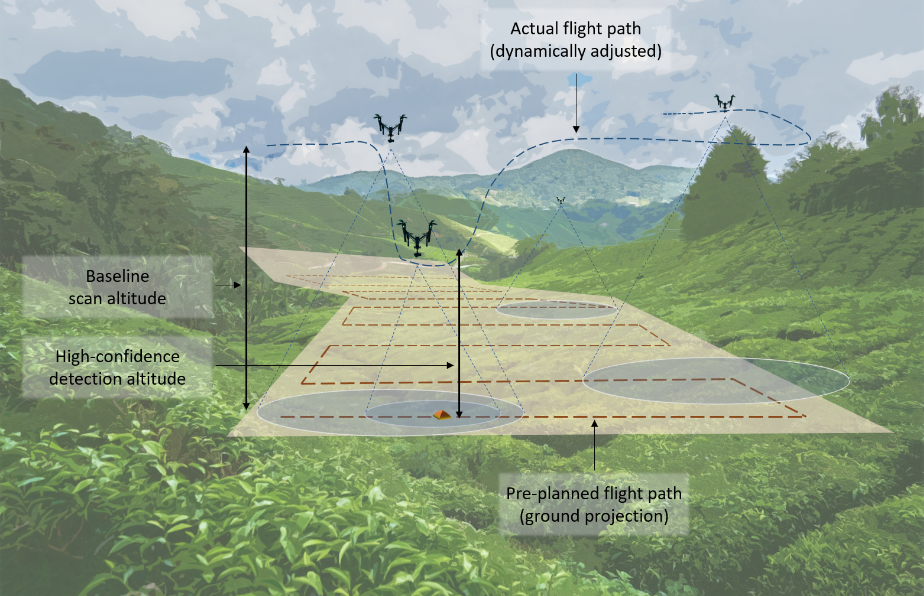 Simulation Analysis of Exploration Strategies and UAV Planning for Search and RescuePhuoc Nguyen Thuan, Jorge Peña Queralta, and Tomi WesterlundIn New Developments and Environmental Applications of Drones, Cham
Simulation Analysis of Exploration Strategies and UAV Planning for Search and RescuePhuoc Nguyen Thuan, Jorge Peña Queralta, and Tomi WesterlundIn New Developments and Environmental Applications of Drones, ChamAerial scans with unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are becoming more widely adopted across industries, from smart farming to urban mapping. An application area that can leverage the strength of such systems is search and rescue (SAR) operations. However, with a vast variability in strategies and topology of application scenarios, as well as the difficulties in setting up real-world UAV-aided SAR operations for testing, designing an optimal flight pattern to search for and detect all victims can be a challenging problem. Specifically, the deployed UAV should be able to scan the area in the shortest amount of time while maintaining high victim detection recall rates. Therefore, low probability of false negatives (i.e., high recall) is more important than precision in this case. To address the issues mentioned above, we have developed a simulation environment that emulates different SAR scenarios and allows experimentation with flight missions to provide insight into their efficiency. The solution was developed with the open-source ROS framework and Gazebo simulator, with PX4 as the autopilot system for flight control, and YOLO as the object detector.
@inproceedings{thuanSimulationAnalysisExploration2024, selected = false, title = {Simulation {{Analysis}} of {{Exploration Strategies}} and { {UAV Planning}} for {{Search}} and {{Rescue}}}, booktitle = {New {{Developments}} and {{Environmental Applications}} of {{Drones}}}, author = {Thuan, Phuoc Nguyen and Queralta, Jorge Peña and Westerlund, Tomi}, editor = {Westerlund, Tomi and Peña Queralta, Jorge}, date = {2024}, pages = {75--84}, publisher = {Springer Nature Switzerland}, location = {Cham}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-031-44607-8_5}, isbn = {978-3-031-44607-8}, langid = {english} }